
The numerous microvilli increase the surface area, making absorption more effective.

This is the point at which any essential substances (such as ions, amino acids, vitamins and glucose) get transported back to the blood. It also filters some useful substances including amino acids and glucose but selective reabsorption allows the body to reabsorb them and keep the electrolyte levels balanced.Īfter the fluid is filtered, it goes into the proximal tubule where it is reabsorbed into the peritubular capillaries. This process removes around 70% of the solutes and water from a person’s blood plasma. Although the smaller molecules in the blood are able to pass through this membrane, larger molecules such as blood cells and proteins cannot. These fibers have a mesh-like structure that uses ultrafiltration to filter the blood. This basement membrane contains collagen and glycoprotein fibers. The glomerulus has two cell layers as well as a basement membrane that separate it from the Bowman’s capsule. The main functions of the nephron are related to filtering, reabsorbing and secreting glutamate, carbohydrates and solutes. Each kidney usually has between 800,000 and 1.5 million nephrons.

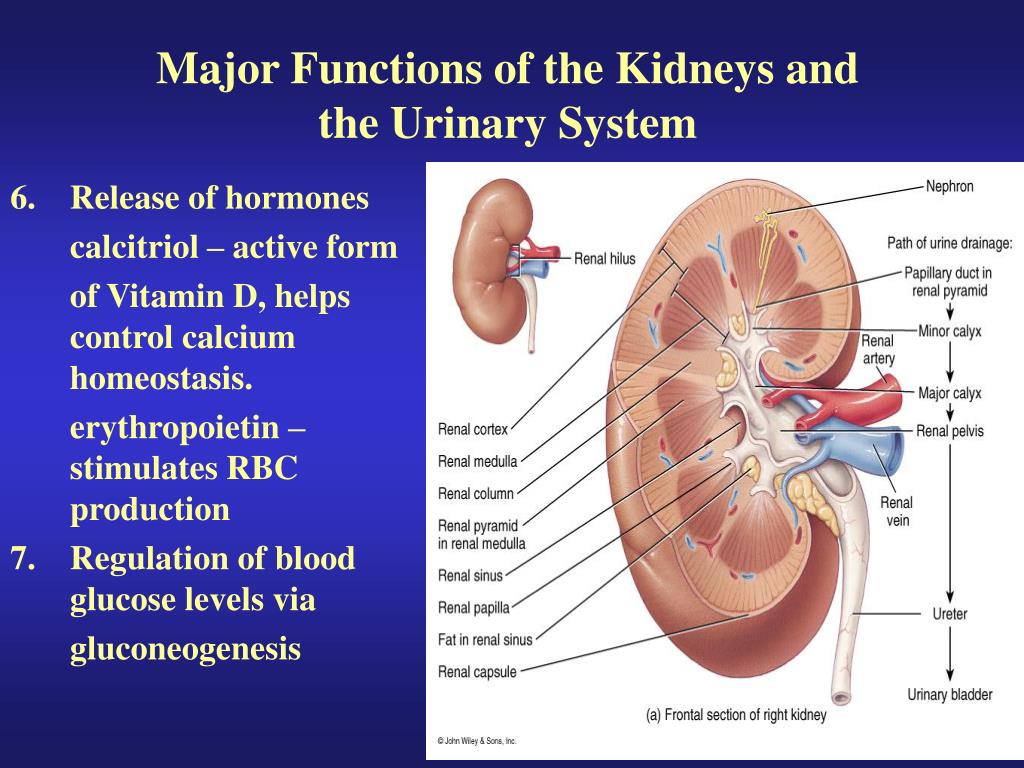
It also regulates blood pressure and volume, controls the levels of metabolites and electrolytes and helps eliminate waste from the body. Its main functions include regulating the concentration of sodium salts and water by filtering the kidney’s blood, excreting any excess in the urine and reabsorbing the necessary amounts. The nephron is the basic functional and structural unit found in the kidneys.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
